
[ad_1]

AMD
Nearly two years after releasing its first Ryzen 5000 desktop processors, AMD is lastly able to comply with them up. Today, the corporate introduced pricing and availability for the primary wave of Ryzen 7000 CPUs primarily based on the Zen 4 structure, together with extra particulars in regards to the accompanying AM5 platform and the efficiency will increase that early adopters can count on.
The first 4 Ryzen 7000 CPUs might be accessible on September 27, and AMD is utilizing the identical technique it used to launch the 5000 collection (in case you’re questioning in regards to the skipped quantity, 6000-series CPUs are solely accessible for laptops). It’s beginning with 4 higher-end, higher-priced elements, whereas lower-end CPUs for mainstream and finances builds will comply with subsequent yr.
| CPU | MSRP | Cores/threads | Clocks (Base/Boost) | Total cache (L2+L3) | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 5 7600X | $299 | 6c/12t | 4.7/5.3 GHz | 38MB (6+32) | 105 W |
| Ryzen 7 7700X | $399 | 8c/16t | 4.5/5.4 GHz | 40MB (8+32) | 105 W |
| Ryzen 9 7900X | $549 | 12c/24t | 4.7/5.6 GHz | 76MB (12+64) | 170 W |
| Ryzen 9 7950X | $699 | 16c/32t | 4.5/5.7 GHz | 80MB (16+64) | 170 W |
AMD is sticking to the identical core counts it used for Zen 3. The entry-level mannequin is the 6-core Ryzen 5 7600X, launching for a similar $299 that the 5600X value in 2020; the 12-core Ryzen 9 7900X can be launching for $549, the identical worth because the Ryzen 9 5900X. The different two chips are slightly cheaper than their Ryzen 5000 counterparts; the 16-core Ryzen 9 7950X launches for $699, $100 lower than the 5950X, whereas the 8-core Ryzen 7 7700X begins at $399, $50 lower than the launch worth for the Ryzen 7 5800X (technically, this is a worth improve over the $299 Ryzen 7 5700X, however that chip wasn’t launched till almost a yr and a half after the 5800X).
AMD
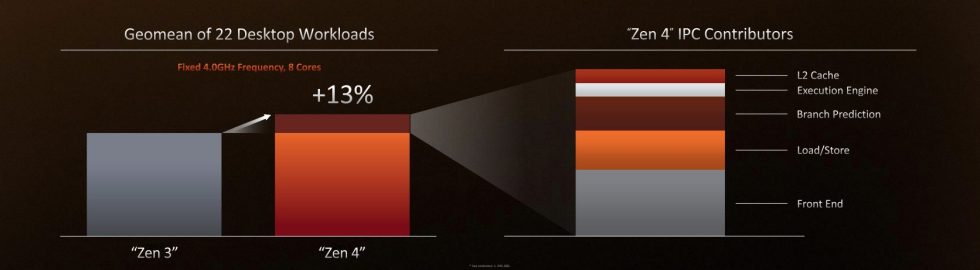
AMD says that “optimizations” remodeled the course of Zen 4’s improvement have elevated its instructions-per-clock (IPC) improve over Zen 3 to a median of 13 p.c, up from the 8–10 p.c improve the corporate promised earlier this yr. The most clock velocity of the 7950X has already elevated to five.7 GHz, 800 MHz sooner than the increase clock of the Ryzen 5950X. All advised, this could make the 7950X a median of 29 p.c sooner than the 5950X at duties that profit from single-threaded efficiency, together with video games.
During its launch occasion and through a Q&A session for media and analysts afterward, AMD hesitated to get too far into the weeds about Zen 4’s structure and pointedly stayed away from projections about after we may count on different Zen 4 chips to launch. But you should not count on 3D V-Cache variations of Zen 4 or lower-end, lower-cost Zen 4 CPUs till someday in 2023.
Performance and energy effectivity good points
AMD
We’ll be taught extra in regards to the adjustments to Zen 4’s structure between now and when the CPUs launch, however the firm shared just a few particulars about the place the efficiency and energy effectivity enhancements are coming from.
AMD Chief Technical Officer Mark Papermaster says that Zen 4 is a revision of the Zen 3 structure that focuses totally on the “entrance finish” of the structure to extra effectively fetch and move duties alongside to the improved execution engine that was the main target of Zen 3. (Papermaster additionally says that Zen 5 might be a extra substantial “floor up” redesign, however we do not count on to listen to many particulars earlier than 2023 or 2024). Most of Zen 4’s 13 p.c IPC increase comes from these optimizations, whereas department prediction, a doubled L2 cache, load/retailer enhancements, and additional small execution engine tweaks account for the remaining.
AMD
Specific duties like machine studying and AI workloads also can profit from the introduction of AVX-512 extensions. This places Intel in an odd spot—the corporate outlined these extensions almost a decade in the past and was alone in pushing them for years. But it has disabled AVX-512 help in its Twelfth-generation CPUs as a result of the processors’ effectivity cores do not help it. These extensions have been a bit controversial as a result of utilizing them can eat a variety of energy and since the workloads that profit from them are specialised and comparatively uncommon (Linux creator Linus Torvalds has mentioned that he hopes “AVX-512 dies a painful loss of life”). But it’s a bit humorous that AMD’s newest CPUs will now help them whereas Intel, the corporate that invented them and pushed to popularize them, sells CPUs that can’t.
-
A greater manufacturing course of (amongst different issues) makes a Zen 4 core a lot smaller than an Intel Golden Cove core (that is the P-core structure for the present Twelfth-gen Alder Lake CPUs and the upcoming Thirteenth-gen Raptor Lake).
AMD -
AMD’s energy effectivity enhancements over Zen 3 are additionally notable, particularly at decrease TDPs. No 65W TDP chips are being launched as we speak, however they need to comply with, given time.
AMD
Even with AVX-512 help added, AMD says {that a} Zen 4 core and its accompanying L2 cache takes up 50 p.c much less space than considered one of Intel’s current-generation P-cores (although that is at the least partly since you’re evaluating TSMC’s 5nm manufacturing course of to the older Intel 7 course of, and partly as a result of a Golden Cove core has 1.25MB of L2 cache whereas a Zen 4 core has a flat 1MB). AMD additionally says a Zen 4 core is “as much as 47 p.c extra energy-efficient” than a Golden Cove core.
AMD additionally makes large claims when evaluating Zen 4 to the previous-generation Zen 3, particularly round performance-per-watt. Comparing the Ryzen 9 7950X to the Ryzen 9 5950X on the identical TDP ranges, AMD says Zen 4 ought to outperform Zen 3 by about 35 p.c when set to a 170W TDP, by about 37 p.c when set to a 105W TDP, and by a whopping 74 p.c when set to a 65W TDP.
This sort of effectivity enchancment is essential, as a result of the CPUs that ship in pre-built OEM methods typically use these decrease inventory TDP ranges relatively than the boosted TDP ranges which might be doable with custom-built methods and extra full-featured motherboards. More effectivity can be helpful for mini-ITX methods, the place you won’t have the cooling capability to let the CPU eat tons of energy and generate tons of warmth.
[ad_2]