
Imagine the next situation. A cellphone rings. An workplace employee solutions it and hears his boss, in a panic, inform him that she forgot to switch cash to the brand new contractor earlier than she left for the day and wishes him to do it. She provides him the wire switch info, and with the cash transferred, the disaster has been averted.
The employee sits again in his chair, takes a deep breath, and watches as his boss walks within the door. The voice on the opposite finish of the decision was not his boss. In reality, it wasn’t even a human. The voice he heard was that of an audio deepfake, a machine-generated audio pattern designed to sound precisely like his boss.
Attacks like this utilizing recorded audio have already occurred, and conversational audio deepfakes may not be far off.
Deepfakes, each audio and video, have been doable solely with the event of refined machine studying applied sciences lately. Deepfakes have introduced with them a brand new degree of uncertainty round digital media. To detect deepfakes, many researchers have turned to analyzing visible artifacts—minute glitches and inconsistencies—present in video deepfakes.
This will not be Morgan Freeman, however for those who weren’t informed that, how would you understand?
Audio deepfakes doubtlessly pose an excellent larger menace, as a result of individuals typically talk verbally with out video—for instance, through cellphone calls, radio, and voice recordings. These voice-only communications vastly increase the probabilities for attackers to make use of deepfakes.
To detect audio deepfakes, we and our analysis colleagues on the University of Florida have developed a way that measures the acoustic and fluid dynamic variations between voice samples created organically by human audio system and people generated synthetically by computer systems.
Organic vs. artificial voices
Humans vocalize by forcing air over the assorted buildings of the vocal tract, together with vocal folds, tongue, and lips. By rearranging these buildings, you alter the acoustical properties of your vocal tract, permitting you to create over 200 distinct sounds, or phonemes. However, human anatomy basically limits the acoustic habits of those totally different phonemes, leading to a comparatively small vary of appropriate sounds for every.
How your vocal organs work.
By distinction, audio deepfakes are created by first permitting a pc to take heed to audio recordings of a focused sufferer speaker. Depending on the precise strategies used, the pc may have to take heed to as little as 10 to twenty seconds of audio. This audio is used to extract key details about the distinctive facets of the sufferer’s voice.
The attacker selects a phrase for the deepfake to talk after which, utilizing a modified text-to-speech algorithm, generates an audio pattern that sounds just like the sufferer saying the chosen phrase. This course of of making a single deepfaked audio pattern might be completed in a matter of seconds, doubtlessly permitting attackers sufficient flexibility to make use of the deepfake voice in a dialog.
Detecting audio deepfakes
The first step in differentiating speech produced by people from speech generated by deepfakes is knowing how you can acoustically mannequin the vocal tract. Luckily scientists have strategies to estimate what somebody—or some being akin to a dinosaur—would sound like based mostly on anatomical measurements of its vocal tract.
We did the reverse. By inverting many of those identical strategies, we have been capable of extract an approximation of a speaker’s vocal tract throughout a phase of speech. This allowed us to successfully peer into the anatomy of the speaker who created the audio pattern.
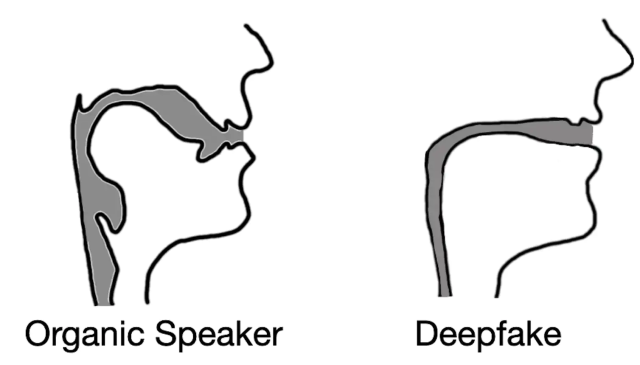
From right here, we hypothesized that deepfake audio samples would fail to be constrained by the identical anatomical limitations people have. In different phrases, the evaluation of deepfaked audio samples simulated vocal tract shapes that don’t exist in individuals.
Our testing outcomes not solely confirmed our speculation however revealed one thing fascinating. When extracting vocal tract estimations from deepfake audio, we discovered that the estimations have been typically comically incorrect. For occasion, it was widespread for deepfake audio to end in vocal tracts with the identical relative diameter and consistency as a ingesting straw, in distinction to human vocal tracts, that are a lot wider and extra variable in form.
This realization demonstrates that deepfake audio, even when convincing to human listeners, is way from indistinguishable from human-generated speech. By estimating the anatomy chargeable for creating the noticed speech, it’s doable to determine whether or not the audio was generated by an individual or a pc.
Why this issues
Today’s world is outlined by the digital change of media and knowledge. Everything from information to leisure to conversations with family members sometimes occurs through digital exchanges. Even of their infancy, deepfake video and audio undermine the arrogance individuals have in these exchanges, successfully limiting their usefulness.
If the digital world is to stay a important useful resource for info in individuals’s lives, efficient and safe strategies for figuring out the supply of an audio pattern are essential.
Logan Blue is a PhD pupil in laptop and knowledge science and engineering on the University of Florida, and Patrick Traynor is professor of laptop and knowledge science and engineering on the University of Florida.
This article is republished from The Conversation underneath a Creative Commons license. Read the unique article.

